Your gut health plays a crucial role in your overall wellness, influencing everything from digestion and immune function to mental clarity and mood. The trillions of microorganisms living in your gut, known as the microbiome, help maintain balance in your body, but they can be disrupted by poor diet, stress, and other lifestyle factors. Thankfully, eating the right foods can support a healthy gut and promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. In this article, we’ll explore the best foods for gut health and how to incorporate them into your diet to nourish your microbiome and improve your overall health.
Why Gut Health Matters
The gut is often referred to as the “second brain” due to its significant influence on various bodily functions, including digestion, nutrient absorption, immune system regulation, and even mental health. A healthy gut is populated with diverse beneficial bacteria that support these processes, but an imbalance in the microbiome, known as dysbiosis, can lead to digestive issues, weakened immunity, inflammation, and mental health disorders.
Eating gut-friendly foods can help promote the growth of healthy bacteria and restore balance, keeping your digestive system running smoothly and your body functioning optimally.
Best Foods for Gut Health
Here are some of the top foods that promote a healthy gut, support digestion, and improve overall well-being.
1. Fermented Foods
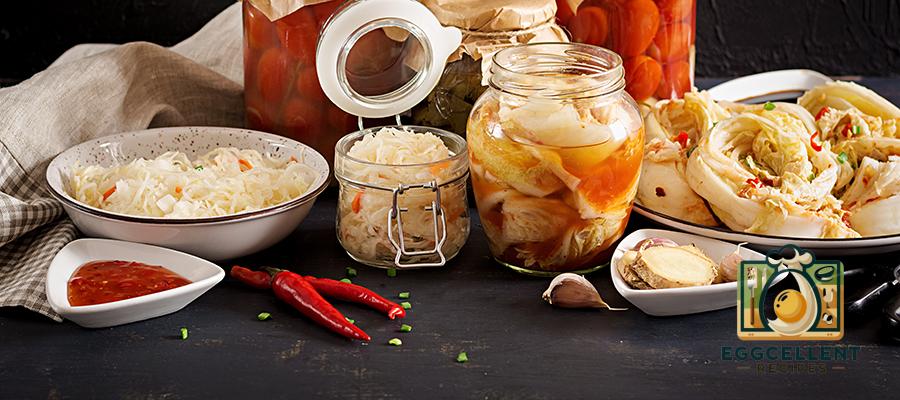

Fermented foods are rich in probiotics, which are live bacteria that promote the growth of beneficial microorganisms in your gut. Incorporating fermented foods into your diet can help restore balance in the gut microbiome and improve digestion.
- Examples of Fermented Foods:
- Yogurt: Contains live cultures like Lactobacillus, which can support gut health and improve digestion.
- Kefir: A fermented milk drink that is high in probiotics and beneficial yeast.
- Sauerkraut: Fermented cabbage rich in probiotics and fiber, which help support healthy digestion.
- Kimchi: A Korean fermented vegetable dish packed with probiotics and fiber.
- Miso: A fermented soybean paste commonly used in Japanese cuisine that provides beneficial bacteria for gut health.
2. Prebiotic-Rich Foods
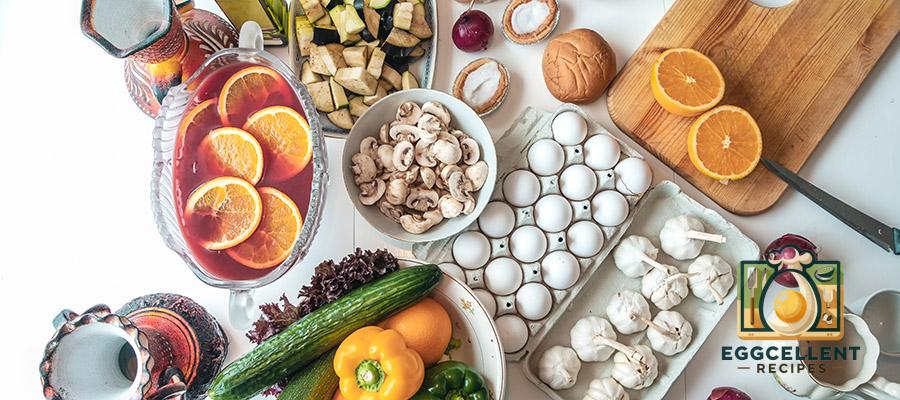

Prebiotics are a type of fiber that acts as food for the beneficial bacteria in your gut. By feeding these bacteria, prebiotics help them thrive and maintain balance in the microbiome.
- Examples of Prebiotic Foods:
- Garlic: Contains inulin, a prebiotic fiber that feeds gut bacteria.
- Onions: Another source of inulin, onions help promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Asparagus: Rich in fiber and prebiotics, asparagus supports the growth of healthy bacteria.
- Bananas: Particularly green, unripe bananas contain prebiotic fiber that supports gut health.
- Leeks: High in prebiotics, leeks are a great addition to soups, salads, and stir-fries to support gut health.
3. Fiber-Rich Foods
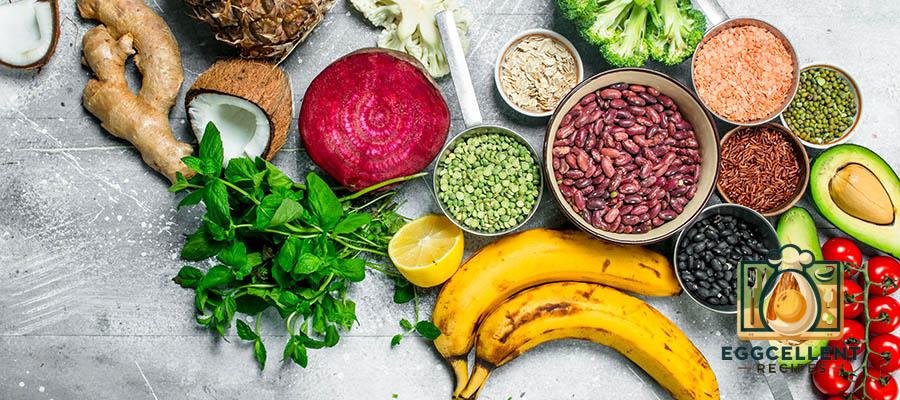

Dietary fiber is essential for gut health, as it adds bulk to stool and supports regular bowel movements. Fiber also serves as food for gut bacteria, promoting the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
- Examples of Fiber-Rich Foods:
- Whole Grains: Brown rice, oats, quinoa, and whole wheat bread are all great sources of fiber that help maintain regular digestion.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas provide both fiber and prebiotics, making them excellent for gut health.
- Berries: Blueberries, raspberries, and blackberries are high in fiber and antioxidants, supporting gut health and overall well-being.
- Apples: High in pectin, a type of soluble fiber, apples can help support healthy digestion.
- Chia Seeds: These tiny seeds are packed with fiber and can help regulate bowel movements.
4. Polyphenol-Rich Foods
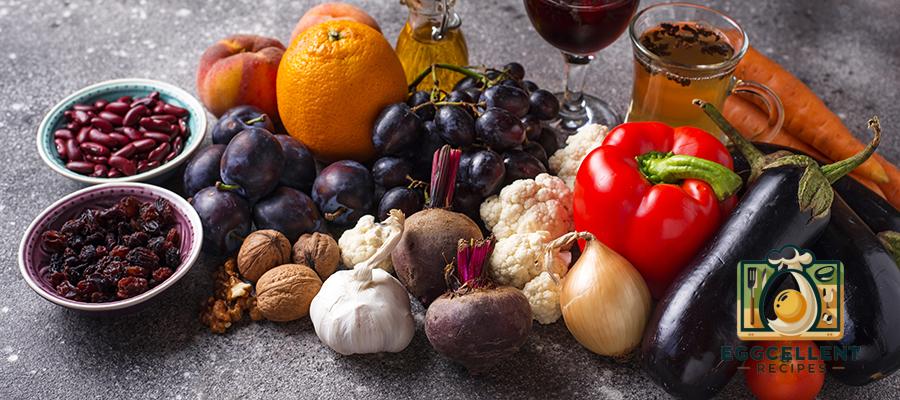

Polyphenols are plant compounds that have antioxidant properties and support the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. They help reduce inflammation in the gut and promote a healthy microbiome.
- Examples of Polyphenol-Rich Foods:
- Dark Chocolate: Rich in polyphenols, dark chocolate may promote the growth of good bacteria in the gut.
- Green Tea: Contains polyphenols called catechins, which can benefit gut health by supporting beneficial bacteria.
- Olive Oil: Extra virgin olive oil contains polyphenols that have anti-inflammatory properties and promote gut health.
- Berries: Strawberries, blueberries, and blackberries are high in polyphenols, which support gut health and overall wellness.
- Red Wine (in moderation): Contains polyphenols that may positively impact gut bacteria, but should be consumed in moderation.
5. Bone Broth
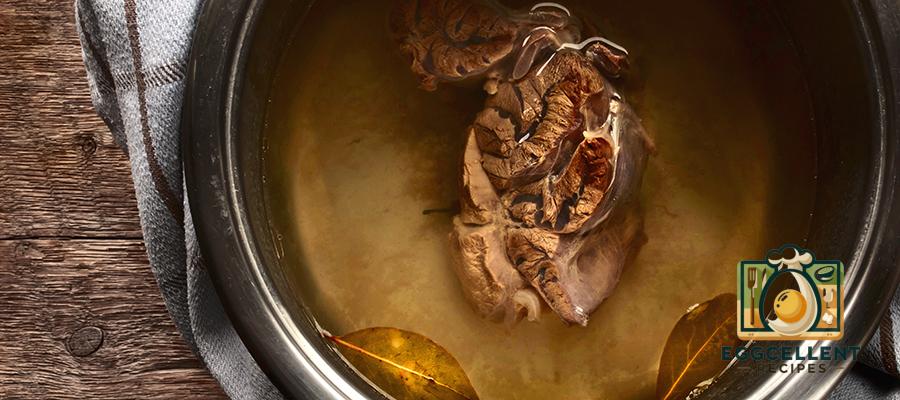

Bone broth is rich in collagen, gelatin, and amino acids like glutamine, which can help heal and support the gut lining. It may be beneficial for individuals with leaky gut syndrome or digestive disorders like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS).
- How to Incorporate Bone Broth:
- Drink it on its own as a warm, nourishing beverage.
- Use it as a base for soups, stews, or sauces.
- Incorporate it into cooking grains like rice or quinoa for added gut support.
6. Ginger
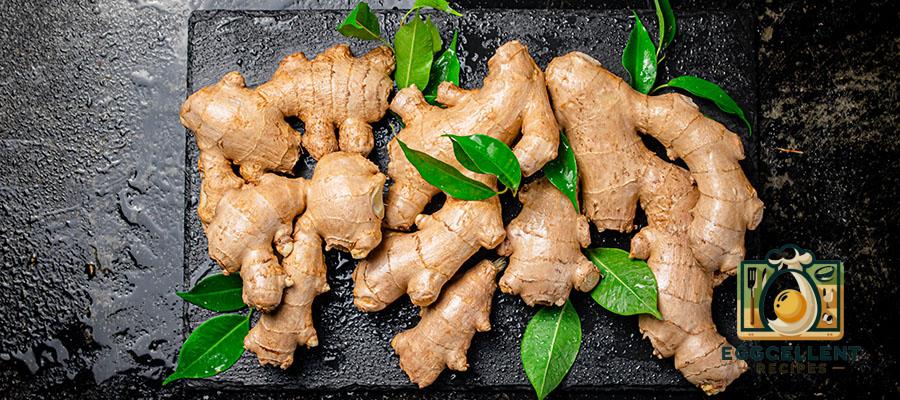

Ginger is well-known for its anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits. It can help reduce bloating, stimulate digestion, and soothe the gut. Ginger has also been found to support gut motility, helping food move through the digestive tract more efficiently.
- How to Use Ginger:
- Add fresh or powdered ginger to teas, smoothies, or stir-fries.
- Include ginger in soups, curries, or dressings for added flavor and gut support.
7. Leafy Greens
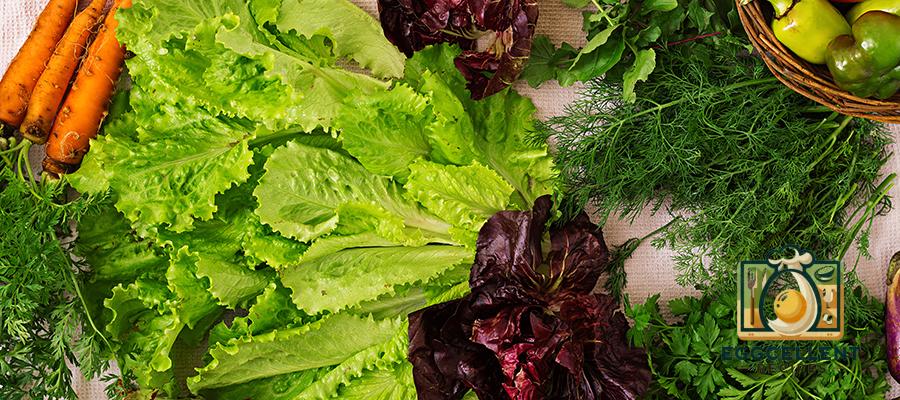

Leafy greens like spinach, kale, and Swiss chard are excellent for gut health due to their high fiber content and abundance of vitamins and minerals. They help feed gut bacteria and promote regular bowel movements.
- How to Incorporate Leafy Greens:
- Add them to salads, smoothies, or stir-fries.
- Use them as a base for grain bowls or soups.
- Try sautéing or steaming them as a side dish with meals.
Tips for Improving Gut Health
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking enough water helps move food through the digestive tract and supports a healthy gut.
- Eat a Diverse Diet: Incorporating a wide variety of plant-based foods ensures that you’re feeding different types of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
- Limit Processed Foods: Processed foods, added sugars, and unhealthy fats can negatively impact gut health by promoting the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Manage Stress: Chronic stress can disrupt the gut microbiome. Practices like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress and improve gut health.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity has been shown to promote healthy gut bacteria and support digestion.
Your gut health is the foundation of your overall well-being, and incorporating gut-friendly foods into your diet can have a significant positive impact on your digestive health, immune system, and even mental clarity. Fermented foods, prebiotics, fiber-rich fruits and vegetables, and polyphenol-rich options like dark chocolate and berries can nourish your microbiome and promote a healthy gut. By making small, consistent changes to your diet and lifestyle, you can support your gut health and improve your long-term wellness.