Hormones are chemical messengers in your body that play a crucial role in regulating various functions, including metabolism, mood, reproductive health, and energy levels. When your hormones are balanced, your body functions smoothly, but when they become imbalanced, it can lead to issues like fatigue, weight gain, mood swings, and more. Fortunately, there are natural ways to help balance your hormones, primarily through diet and lifestyle changes. In this article, we’ll explore how to balance hormones naturally and what foods you should eat to support hormonal health.
Understanding Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal imbalances can occur due to various factors, including stress, poor diet, lack of sleep, age, and environmental toxins. Common symptoms of hormonal imbalances include:
- Fatigue or low energy
- Weight gain or difficulty losing weight
- Irregular menstrual cycles
- Mood swings, anxiety, or depression
- Low libido
- Sleep disturbances
Balancing your hormones naturally is a holistic approach that focuses on diet, lifestyle changes, and reducing stress. The right foods can have a significant impact on hormone production and regulation, helping to restore balance and improve your overall well-being.
Key Nutrients for Hormonal Balance
Certain nutrients are particularly beneficial for hormone production and regulation. These include:
- Healthy Fats: Hormones are made from cholesterol and fats, so eating enough healthy fats is essential for hormonal health.
- Protein: Provides amino acids necessary for hormone production and supports blood sugar balance.
- Fiber: Helps detoxify excess hormones from the body, particularly estrogen.
- Vitamins and Minerals: Micronutrients like magnesium, zinc, and B vitamins are important for hormone synthesis and balance.
Foods to Eat for Hormonal Balance
1. Avocados

Avocados are rich in healthy monounsaturated fats, which are essential for hormone production. These fats also help reduce inflammation and support the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like vitamin A, D, E, and K, all of which are vital for hormone regulation.
2. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel, Sardines)
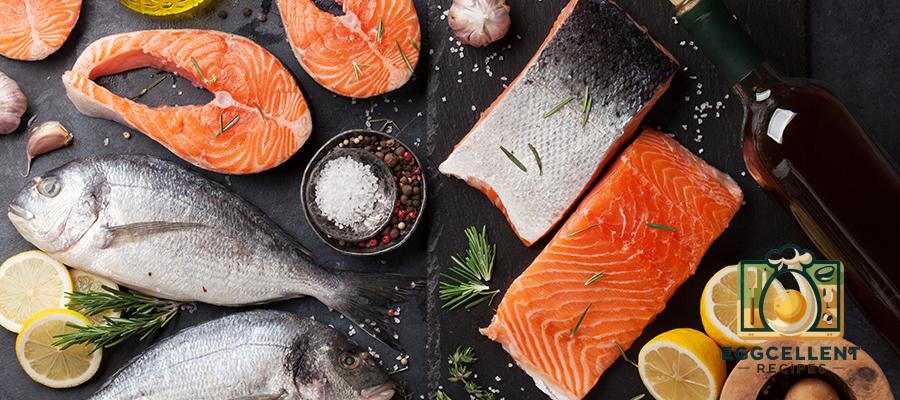

Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are excellent sources of omega-3 fatty acids. Omega-3s help reduce inflammation, balance hormones like cortisol (the stress hormone), and support the production of reproductive hormones. These healthy fats are also beneficial for brain health, mood, and overall hormonal function.
3. Leafy Greens (Spinach, Kale, Swiss Chard)
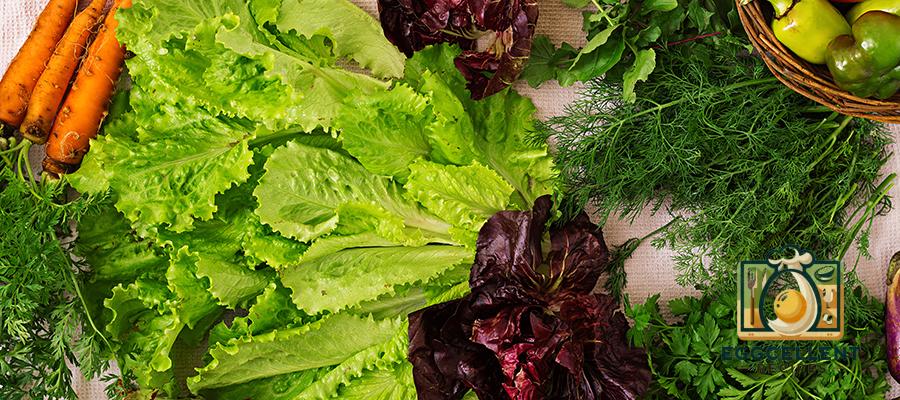

Leafy greens are packed with vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which help balance hormones by supporting liver function and detoxifying excess hormones. They are also rich in magnesium, a mineral that plays a crucial role in hormone regulation, particularly in reducing symptoms of PMS and balancing cortisol levels.
4. Cruciferous Vegetables (Broccoli, Cauliflower, Brussels Sprouts)
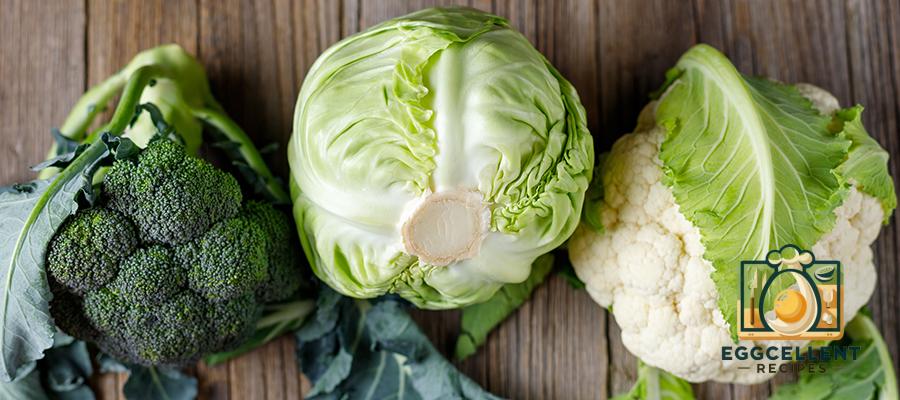

Cruciferous vegetables contain compounds like indole-3-carbinol, which support the liver in metabolizing and detoxifying excess estrogen, helping to prevent estrogen dominance. They are also high in fiber, which aids in hormone regulation by promoting healthy digestion and preventing constipation.
5. Nuts and Seeds (Flaxseeds, Chia Seeds, Walnuts)
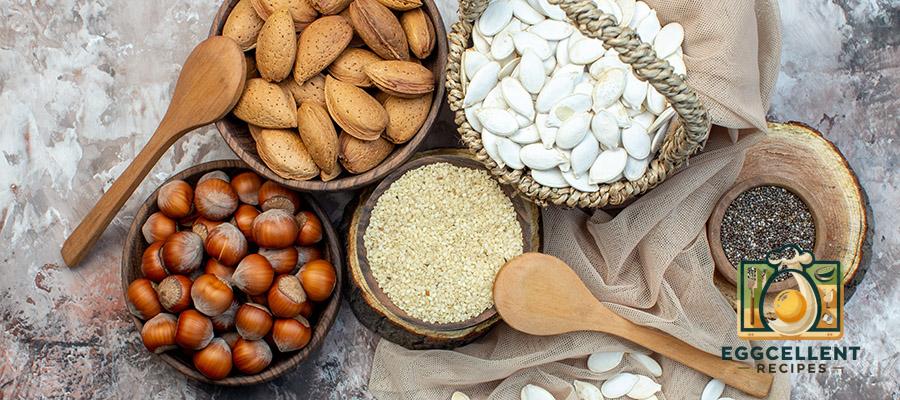

Nuts and seeds provide healthy fats, fiber, and important nutrients like zinc and selenium, which support hormone production and balance. Flaxseeds, in particular, contain lignans, which help regulate estrogen levels, making them beneficial for women experiencing hormonal fluctuations related to menstruation or menopause.
6. Eggs
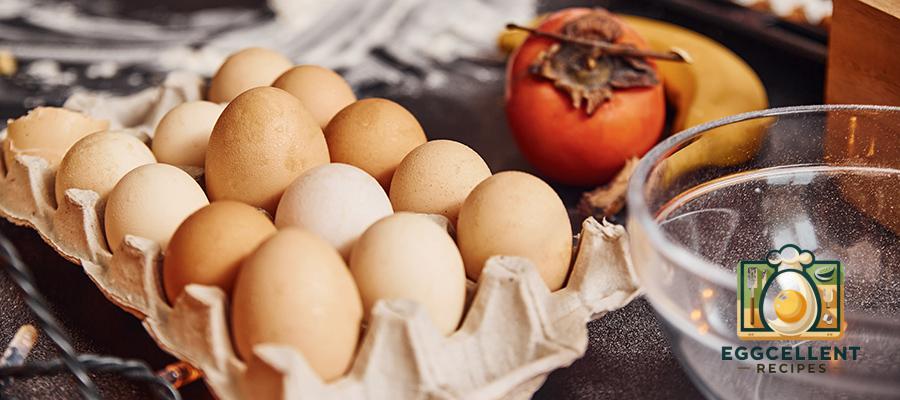

Eggs are a fantastic source of high-quality protein and healthy fats, both of which are essential for hormone production. The yolk contains important nutrients like vitamin D, which plays a role in regulating sex hormones and maintaining bone health.
7. Berries (Blueberries, Raspberries, Strawberries)
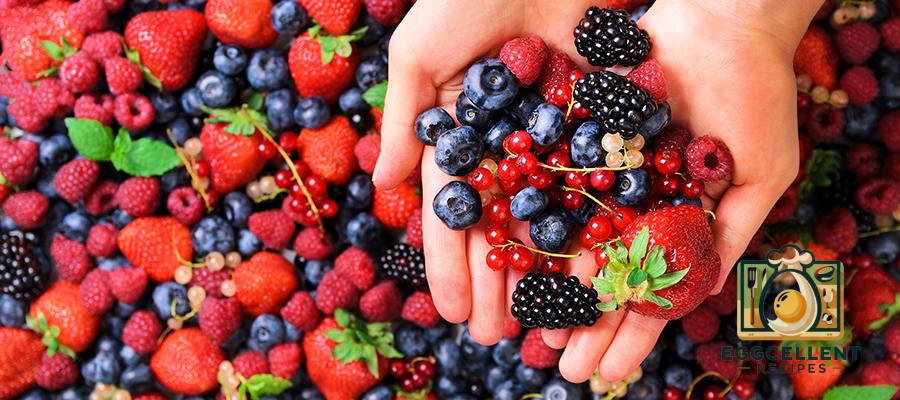

Berries are rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and fiber, which help reduce inflammation and support hormonal balance. Their high fiber content helps regulate blood sugar levels, preventing insulin spikes that can disrupt hormones.
8. Coconut Oil
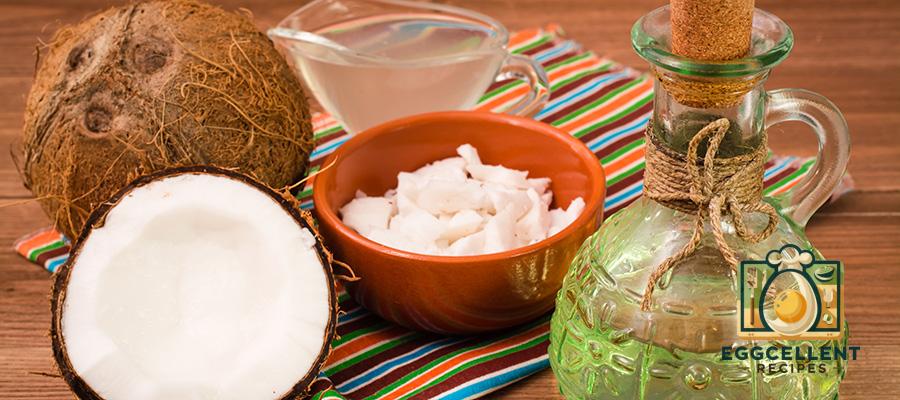

Coconut oil is a healthy fat that can help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce inflammation, and support thyroid health. The medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) in coconut oil are easily digested and used for energy, helping to balance hormone production.
9. Quinoa
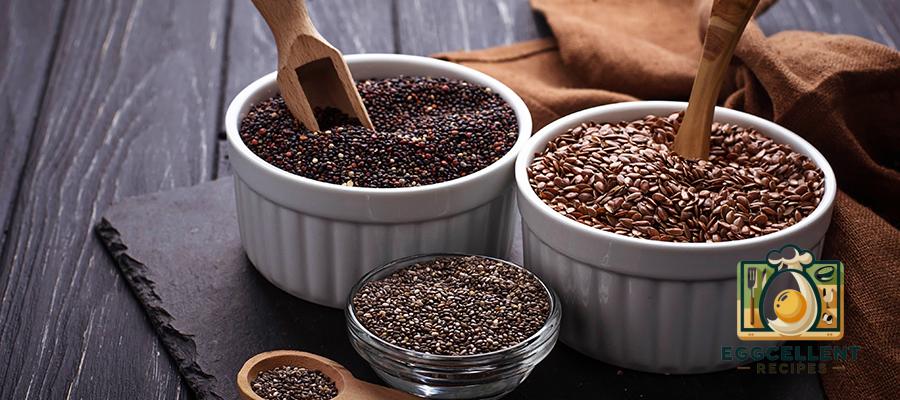

Quinoa is a high-protein, gluten-free grain that provides a good source of fiber and essential amino acids. It helps balance blood sugar levels, which is important for preventing insulin resistance—a condition that can lead to hormonal imbalances.
10. Greek Yogurt

Greek yogurt is rich in probiotics, which support gut health and the microbiome. Since your gut plays a significant role in hormone regulation, consuming probiotic-rich foods can improve digestion and help balance hormones, especially estrogen.
Lifestyle Tips for Hormonal Balance
In addition to eating the right foods, adopting healthy lifestyle habits is key to balancing your hormones naturally.
1. Manage Stress

Chronic stress can wreak havoc on your hormones, especially cortisol and insulin. Stress management techniques such as yoga, meditation, deep breathing exercises, and regular physical activity can help reduce cortisol levels and support overall hormone balance.
2. Stay Active

Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining a healthy hormonal balance. It can help reduce stress, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote the production of endorphins (feel-good hormones). Strength training and aerobic exercises are particularly effective in balancing hormones like cortisol and testosterone.
3. Stay Hydrated

Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps flush toxins from your body and supports proper digestion and metabolism. Dehydration can stress your body and lead to imbalanced hormones, so aim to drink at least 8 cups of water daily.
4. Limit Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors

Endocrine disruptors are chemicals found in many everyday products, such as plastics, personal care items, and cleaning products, that can interfere with your hormone system. These chemicals, including bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, and parabens, can mimic or block hormones and cause imbalances. To reduce your exposure:
- Use glass or stainless steel containers instead of plastic for food storage and drinking.
- Choose natural or organic personal care products free from synthetic fragrances, parabens, and phthalates.
- Avoid heating food in plastic containers, as heat can cause harmful chemicals to leach into your food.
- Opt for eco-friendly cleaning products or make your own with simple ingredients like vinegar and baking soda.
5. Maintain a Healthy Gut

Your gut plays a critical role in hormone regulation, especially in the detoxification of excess hormones, such as estrogen. A healthy gut helps maintain balanced hormone levels, while an unhealthy gut can contribute to imbalances. To support your gut health:
- Eat probiotic-rich foods, such as yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi, and kefir, to promote healthy gut bacteria.
- Increase fiber intake from fruits, vegetables, and whole grains to help detoxify excess hormones.
- Limit processed foods and added sugars, which can harm gut bacteria and promote inflammation.
A healthy gut not only improves digestion but also aids in maintaining overall hormonal balance.
6. Monitor Caffeine and Alcohol Intake

Excessive caffeine and alcohol consumption can disrupt hormone levels, particularly by increasing cortisol (the stress hormone) and affecting sleep. Moderating your intake of these substances can support hormonal health:
- Caffeine: While a moderate amount of caffeine is generally safe, too much can elevate cortisol levels, leading to stress and poor sleep quality. Consider switching to green tea or herbal teas for a gentler boost.
- Alcohol: Drinking too much alcohol can interfere with the liver’s ability to detoxify hormones, particularly estrogen. Aim to limit alcohol consumption to moderate levels, such as one drink per day for women or two drinks per day for men.
7. Focus on Blood Sugar Balance
Keeping your blood sugar stable is crucial for hormonal health, particularly in managing insulin levels. Blood sugar spikes and crashes can lead to insulin resistance, which disrupts other hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. To balance blood sugar:
- Eat balanced meals that contain protein, healthy fats, and fiber to slow down the absorption of sugars and prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Avoid refined carbohydrates and sugary snacks, which cause rapid increases in blood sugar.
- Eat regular meals to prevent hunger and stabilize blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Balancing blood sugar helps prevent energy crashes, supports weight management, and reduces stress on the endocrine system.
8. Practice Mindful Eating

Hormonal health is closely linked to how and when you eat. Practicing mindful eating can help regulate hormones related to hunger, stress, and digestion. Tips for mindful eating include:
- Eat slowly and chew thoroughly, allowing your body time to properly digest food and send signals of fullness.
- Avoid eating while distracted, such as watching TV or working, so that you can tune into your hunger and fullness cues.
- Focus on balanced meals, incorporating whole, nutrient-dense foods that support hormonal health.
Mindful eating also helps reduce overeating, supports digestion, and balances blood sugar levels.
9. Get Regular Sunlight Exposure
Sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D, which is essential for hormone production, particularly for testosterone, estrogen, and thyroid hormones. Many people are deficient in vitamin D, which can lead to hormonal imbalances. Regular sunlight exposure can help maintain adequate vitamin D levels, promoting overall hormonal health.
- Spend at least 15-20 minutes a day in direct sunlight, especially during peak hours in the morning or late afternoon.
- Consider a vitamin D supplement if you live in a region with limited sunlight or during the winter months.
Getting enough sunlight can also improve your mood and help regulate your sleep-wake cycle, which is vital for hormone balance.
10. Maintain a Regular Sleep Schedule
In addition to getting enough sleep, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule is important for hormone regulation. Irregular sleep patterns can disrupt the production of hormones like melatonin and cortisol, affecting your body’s natural rhythm. To support balanced hormone production:
- Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day, even on weekends.
- Create a calming bedtime routine, such as reading or meditating, to signal to your body that it’s time to sleep.
- Avoid exposure to blue light from phones, computers, and TVs at least an hour before bed, as it can interfere with melatonin production.
Consistency in your sleep routine helps regulate hormones that control energy levels, stress, and appetite.
Final Thoughts
Balancing your hormones naturally requires a combination of healthy eating, regular physical activity, stress management, and quality sleep. By incorporating nutrient-dense, hormone-supporting foods such as healthy fats, lean proteins, and fiber-rich vegetables into your diet, you can help restore hormonal harmony and improve your overall health.
Remember, hormones play a vital role in your body’s daily functions, and taking care of your diet and lifestyle will ensure they remain in balance. If you suspect a serious hormonal imbalance, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare provider or endocrinologist to determine the best course of action for your individual needs.