Menopause is a natural phase in every woman’s life, marking the end of menstruation and the reproductive years. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55 but can vary widely among individuals. Understanding the symptoms of menopause is crucial to navigating this transition with confidence and ease.
Below, we explore the common signs of menopause, why they occur, and strategies for managing them effectively.
What is Menopause?
Menopause is defined as the absence of menstrual periods for 12 consecutive months, signaling the end of a woman’s ovarian function. It is preceded by a phase called perimenopause, during which hormonal changes gradually lead to menopause.
The key hormonal shift during this time is a decline in estrogen and progesterone production, which triggers a range of physical and emotional symptoms.
Common Symptoms of Menopause
1. Irregular Periods

Before menstruation ceases entirely, cycles may become unpredictable. Periods might be lighter or heavier, shorter or longer, and more or less frequent.
- Why it happens: Hormonal fluctuations affect ovulation, leading to irregular cycles.
2. Hot Flashes
Hot flashes are sudden sensations of heat, often accompanied by sweating and redness in the face and neck.
- Why it happens: Decreased estrogen levels impact the hypothalamus, the part of the brain responsible for regulating body temperature.
3. Night Sweats
Night sweats are hot flashes that occur during sleep, often disrupting rest and leading to fatigue.
- Why it happens: Hormonal changes affect the body’s ability to regulate temperature.
4. Mood Swings

Irritability, anxiety, or depression can emerge during menopause.
- Why it happens: Fluctuating hormones influence brain chemistry and emotional stability.
5. Sleep Disturbances

Many women experience insomnia or wake frequently during the night.
- Why it happens: Night sweats, anxiety, and other physical discomforts disrupt sleep patterns.
6. Vaginal Dryness
Decreased estrogen levels can lead to thinning and drying of the vaginal tissue, causing discomfort or pain during intercourse.
- Why it happens: Reduced estrogen impacts the production of natural lubrication.
7. Weight Gain

Hormonal changes often lead to weight gain, particularly around the midsection.
- Why it happens: Slower metabolism and changes in fat distribution occur as estrogen levels decline.
8. Decreased Libido
A loss of sexual desire is a common symptom, often linked to physical discomfort and hormonal shifts.
- Why it happens: Lower estrogen levels influence arousal and sensitivity.
9. Thinning Hair and Dry Skin
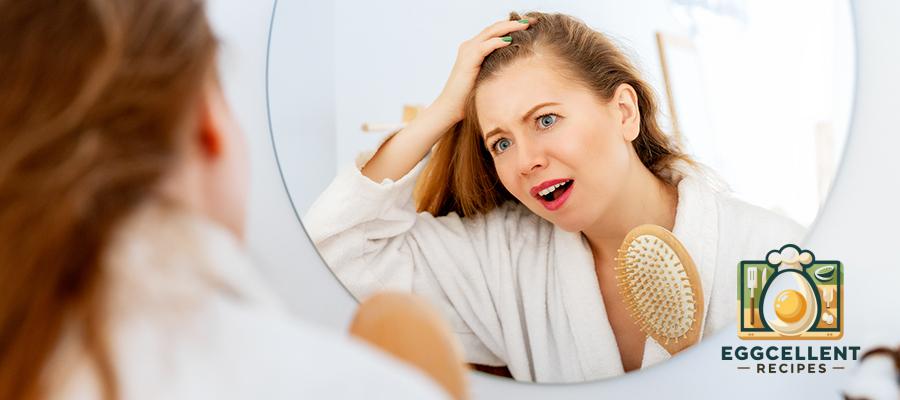

Hair may become finer and thinner, while skin may lose elasticity and moisture.
- Why it happens: Estrogen helps maintain healthy hair and skin, so its decline impacts these features.
10. Memory Problems and Brain Fog
Difficulty concentrating and forgetfulness are often reported during menopause.
- Why it happens: Hormonal changes affect cognitive function and mental clarity.
11. Joint Pain and Stiffness
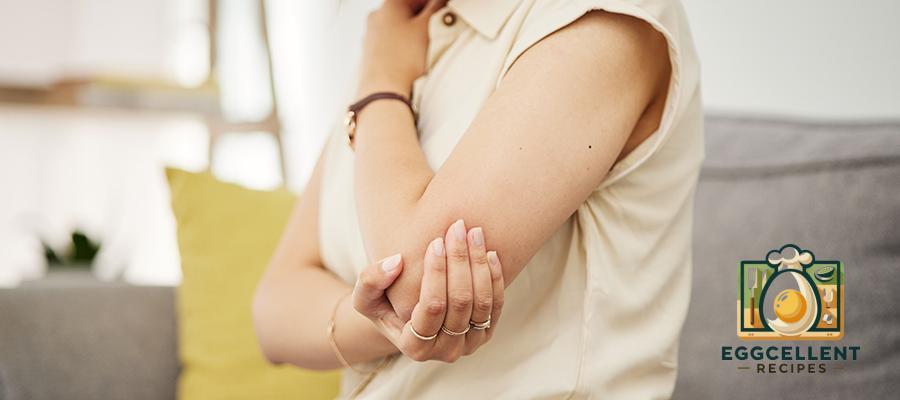

Aching or stiff joints may develop, even without previous issues.
- Why it happens: Declining estrogen levels can contribute to inflammation.
12. Changes in Cholesterol Levels
Menopause can increase LDL (bad cholesterol) and lower HDL (good cholesterol), raising the risk of heart disease.
- Why it happens: Estrogen plays a role in maintaining healthy cholesterol levels.
How to Cope with Menopausal Symptoms
1. Maintain a Healthy Diet
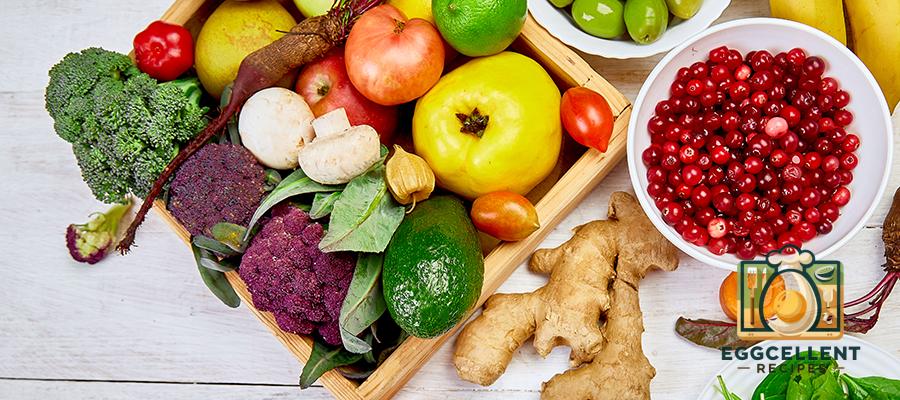

- Eat foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone health.
- Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and whole grains for balanced nutrition.
- Avoid triggers like caffeine and alcohol, which can exacerbate hot flashes and night sweats.
2. Exercise Regularly
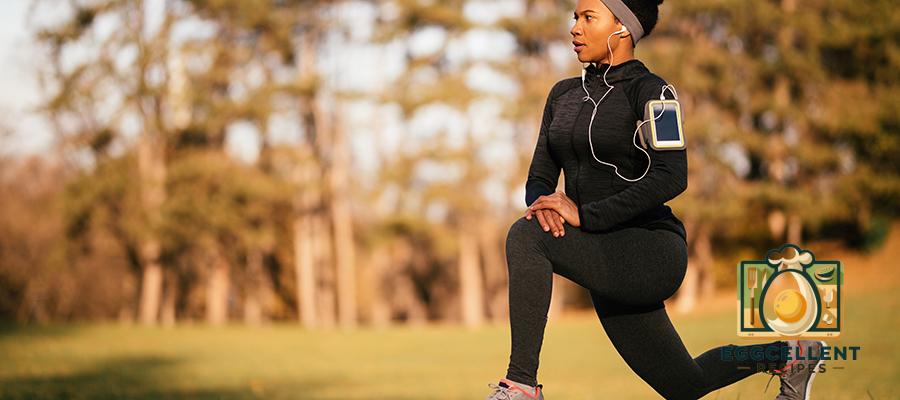

- Engage in weight-bearing exercises to strengthen bones and manage weight.
- Incorporate activities like yoga or Pilates to improve flexibility and reduce stress.
3. Prioritize Sleep
- Establish a bedtime routine to promote better sleep.
- Keep your bedroom cool and comfortable to minimize the impact of night sweats.
4. Stay Hydrated

- Drink plenty of water to combat dryness and bloating.
5. Manage Stress

- Practice mindfulness, meditation, or deep breathing to reduce anxiety and mood swings.
6. Consider Medical Options
- Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) may be an option for severe symptoms.
- Non-hormonal treatments, such as antidepressants or vaginal lubricants, can also provide relief.
7. Seek Support

- Join support groups or talk to friends and family who can provide understanding and encouragement.
When to See a Doctor
If menopausal symptoms significantly affect your quality of life, consult a healthcare provider. They can offer personalized advice and discuss treatment options tailored to your needs.
Be sure to report:
- Very heavy or prolonged periods.
- Unexplained weight changes.
- Severe mood swings or depression.
Embracing the Transition
Menopause is a natural stage in life, and while its symptoms can be challenging, it’s also an opportunity to focus on health and well-being. By understanding the signs and implementing effective coping strategies, women can navigate this transition with resilience and grace.
Remember, menopause marks not an end but a new chapter—one that can be approached with confidence and self-care.