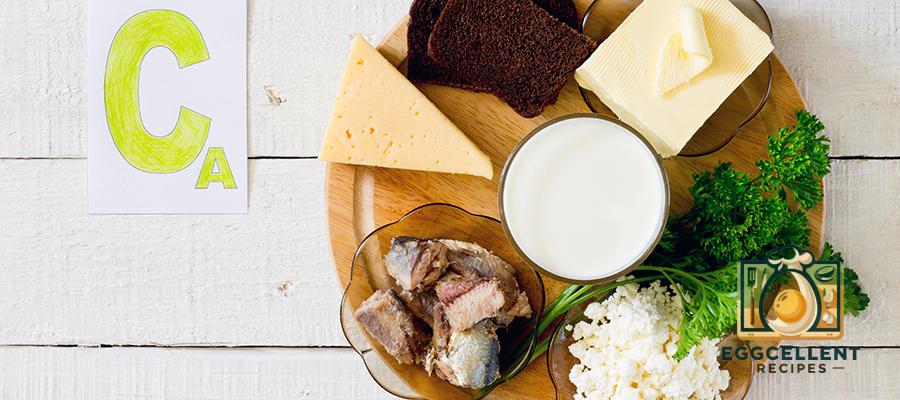
Calcium is an essential mineral that plays a vital role in maintaining strong bones, supporting muscle function, and regulating nerve activity. While dairy products are often associated with calcium, there are many other food sources—both plant-based and animal-based—that can help you meet your daily calcium needs. Whether you follow a dairy-rich diet or prefer plant-based alternatives, this guide covers the best calcium-rich foods to keep your bones and body strong.
Why Is Calcium Important?
Calcium is vital for several key functions in the body, including:
✔ Building and maintaining strong bones and teeth
✔ Supporting muscle contractions and preventing cramps
✔ Aiding in proper nerve function and brain signaling
✔ Regulating blood clotting and heart function
✔ Reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures
How Much Calcium Do You Need?
The recommended daily intake (RDI) for calcium varies by age and gender:
- Children (4–8 years): 1,000 mg
- Teens (9–18 years): 1,300 mg
- Adults (19–50 years): 1,000 mg
- Women over 50 & Men over 70: 1,200 mg
If you don’t get enough calcium, your body will pull it from your bones, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures over time.
Top Calcium-Rich Foods
1. Dairy Products (High in Absorbable Calcium)
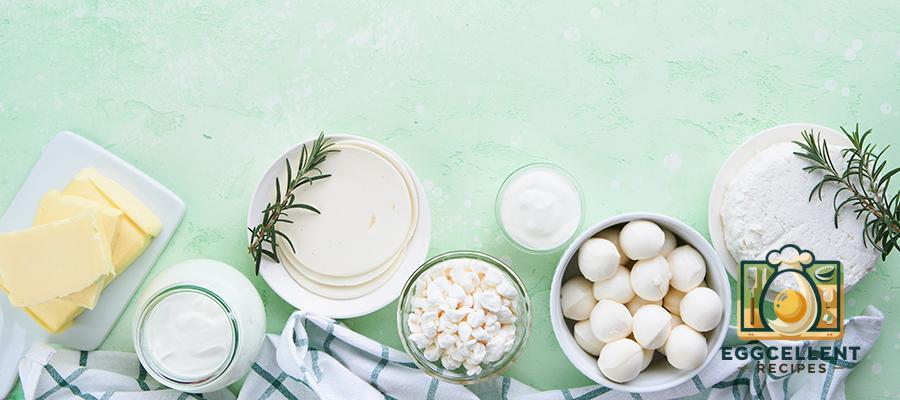

Dairy is one of the richest sources of calcium and contains other essential nutrients like vitamin D and protein, which help with calcium absorption.
- Milk (1 cup): 300 mg
- Cheese (1 oz of cheddar): 200 mg
- Greek Yogurt (1 cup): 250–450 mg
- Cottage Cheese (1 cup): 200 mg
💡 Tip: Choose unsweetened yogurt or full-fat dairy to avoid added sugars and maximize nutrition.
2. Leafy Greens & Vegetables

Many vegetables provide a good amount of calcium, though some contain compounds that affect absorption.
- Collard Greens (1 cup cooked): 268 mg
- Bok Choy (1 cup cooked): 160 mg
- Kale (1 cup raw): 100 mg
- Broccoli (1 cup cooked): 62 mg
- Spinach (1 cup cooked): 250 mg (but less absorbed due to oxalates)
💡 Tip: Cooking low-oxalate greens like kale and bok choy helps boost calcium absorption.
3. Plant-Based Calcium Sources (Great for Vegans & Dairy-Free Diets)
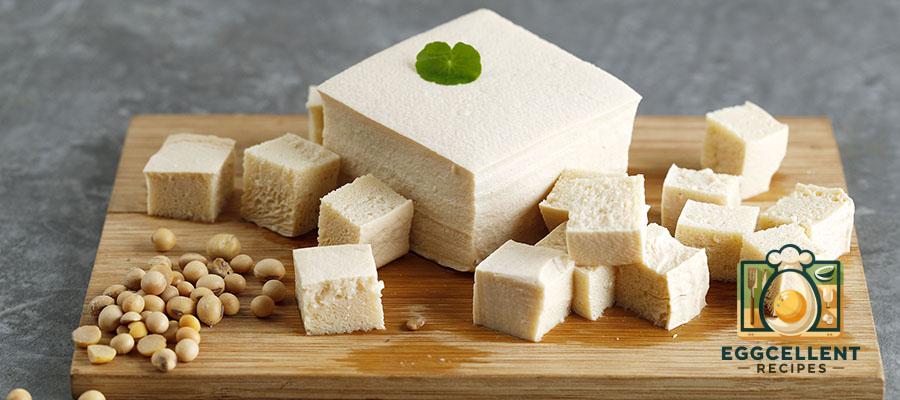

Many plant-based foods provide excellent calcium, making them great alternatives to dairy.
- Tofu (½ cup, calcium-set): 400–600 mg
- Chia Seeds (1 tbsp): 80 mg
- Sesame Seeds (1 tbsp): 90 mg
- Tahini (2 tbsp): 130 mg
- Almonds (1 oz or about 23 almonds): 75 mg
💡 Tip: Calcium-set tofu is made with calcium sulfate, providing more absorbable calcium.
4. Calcium-Fortified Foods
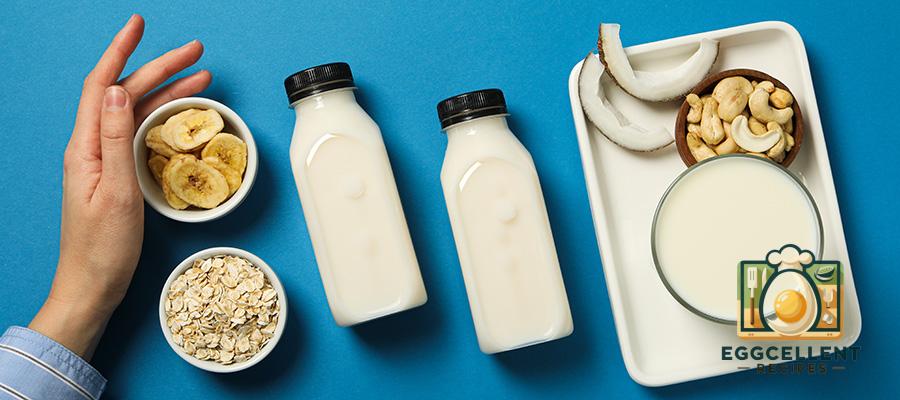

Many foods are fortified with calcium, helping people meet their daily intake.
- Fortified Plant-Based Milk (1 cup almond, soy, oat, or coconut milk): 300–450 mg
- Fortified Orange Juice (1 cup): 350 mg
- Fortified Cereal (1 serving): 200–1,000 mg
- Fortified Bread (1 slice): 100 mg
💡 Tip: Check labels to ensure products contain calcium carbonate, which is better absorbed than other calcium additives.
5. Seafood & Fish (Rich in Calcium & Omega-3s)
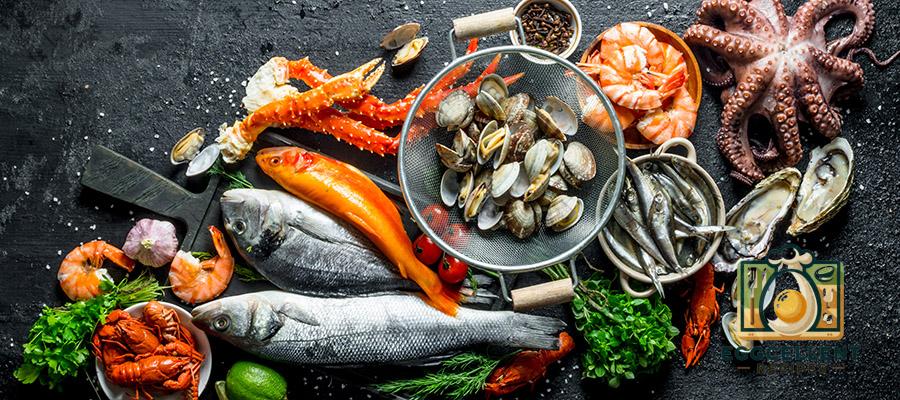

Certain fish provide high amounts of calcium, especially when consumed with bones.
- Canned Sardines (with bones, 3 oz): 325 mg
- Canned Salmon (with bones, 3 oz): 180 mg
- Shrimp (3 oz): 125 mg
💡 Tip: Canned fish with bones is an excellent source of calcium and omega-3 fatty acids.
How to Improve Calcium Absorption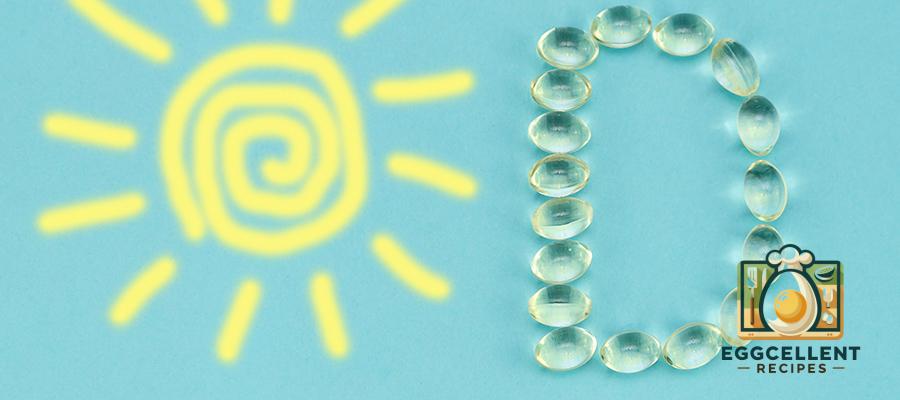
Even if you consume enough calcium, your body may not absorb it efficiently. Here are some tips to improve calcium absorption:
✅ Get Enough Vitamin D – This vitamin helps your body absorb calcium effectively. Get it from:
- Sunlight exposure (15–30 minutes daily)
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, sardines)
- Fortified dairy and plant-based milk
✅ Balance Calcium with Magnesium & Vitamin K – These nutrients help calcium work properly in the body.
- Magnesium sources: Nuts, seeds, whole grains, dark leafy greens
- Vitamin K sources: Leafy greens, fermented foods (sauerkraut, natto)
✅ Limit Excess Salt & Caffeine – Too much sodium and caffeine can cause calcium loss through urine.
Signs of Calcium Deficiency
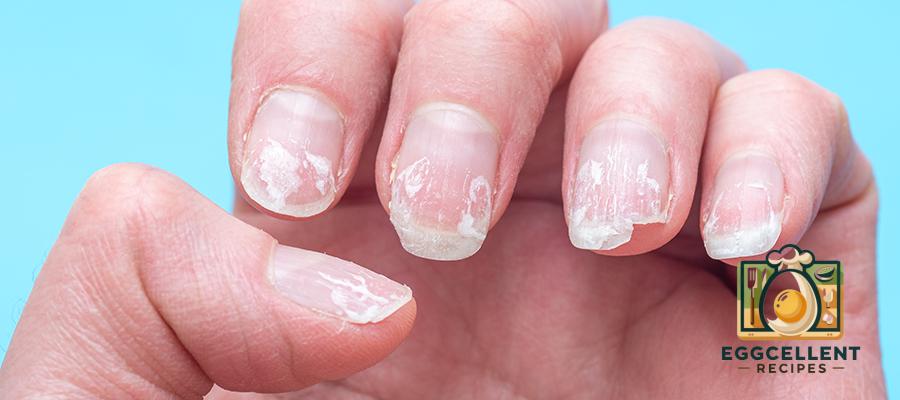
A lack of calcium can lead to health problems over time. Signs of deficiency include:
❌ Frequent muscle cramps or spasms
❌ Brittle nails and weak teeth
❌ Fatigue and low energy levels
❌ Osteoporosis or bone fractures
❌ Tingling sensations in fingers and toes
If you suspect a calcium deficiency, consult a healthcare provider to determine whether you need dietary changes or supplementation.
Final Thoughts
Calcium is essential for bone health, muscle function, and overall well-being. Whether you prefer dairy, plant-based sources, or seafood, there are plenty of ways to meet your daily needs. Pair calcium-rich foods with vitamin D, magnesium, and other supportive nutrients to maximize absorption and prevent deficiencies.
If you have dietary restrictions or concerns about your calcium intake, consider working with a healthcare provider or dietitian to create a personalized meal plan.
Would you like calcium-rich meal ideas or recipes? Let me know! 😊