Gluten intolerance, also known as non-celiac gluten sensitivity (NCGS), is a condition in which individuals experience adverse reactions to gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. Unlike celiac disease, gluten intolerance does not cause immune system damage to the small intestine, but it can still lead to uncomfortable and disruptive symptoms. Recognizing the early warning signs can help you determine whether gluten is affecting your health.
What Is Gluten Intolerance?
Gluten intolerance is a digestive condition where the body has difficulty processing gluten. It is different from celiac disease, which is an autoimmune disorder, and wheat allergy, which involves an allergic reaction to wheat proteins. If left unaddressed, gluten intolerance can cause chronic inflammation, digestive issues, and systemic symptoms that affect overall well-being.
Common Early Signs of Gluten Intolerance
1. Digestive Discomfort
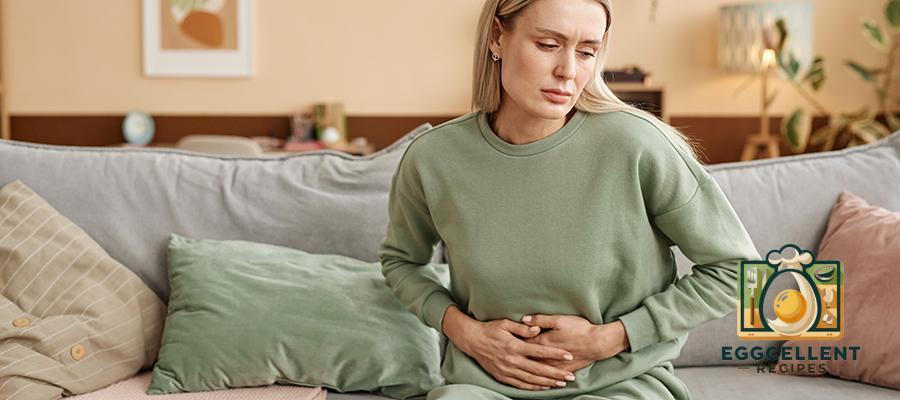

- Bloating after eating gluten-containing foods
- Abdominal pain or cramping
- Gas and indigestion
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Nausea, especially after consuming bread, pasta, or baked goods
Why it happens: Gluten can cause irritation and inflammation in the digestive tract of sensitive individuals, leading to discomfort and irregular bowel movements.
2. Fatigue and Brain Fog
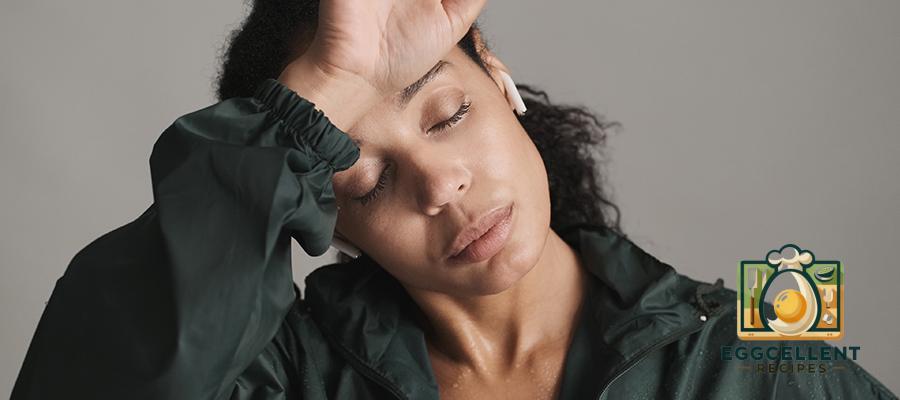

- Feeling constantly tired, even after a full night’s sleep
- Difficulty concentrating or memory issues
- Feeling sluggish or mentally drained
Why it happens: Gluten intolerance can trigger inflammation, which may lead to mental fog, headaches, and low energy levels. Many people report feeling clearer and more focused after removing gluten from their diet.
3. Headaches and Migraines
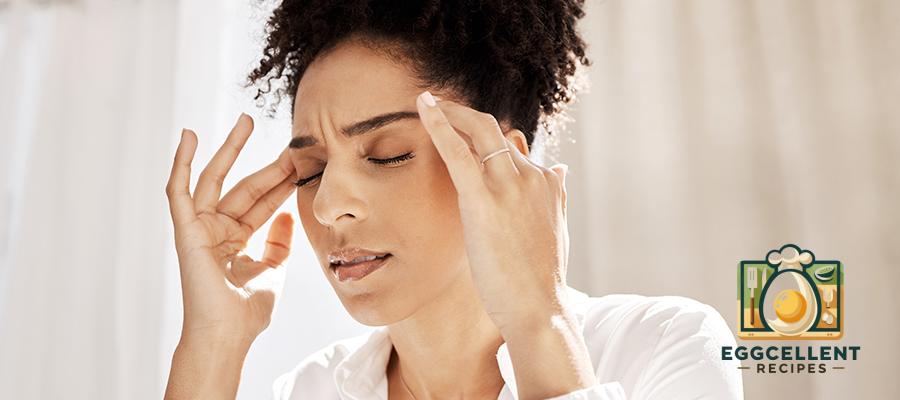

- Frequent tension headaches
- Severe migraines with nausea or sensitivity to light and sound
- Unexplained headaches that occur after meals
Why it happens: Inflammation caused by gluten sensitivity can lead to neurological symptoms, including migraines and headaches.
4. Joint and Muscle Pain
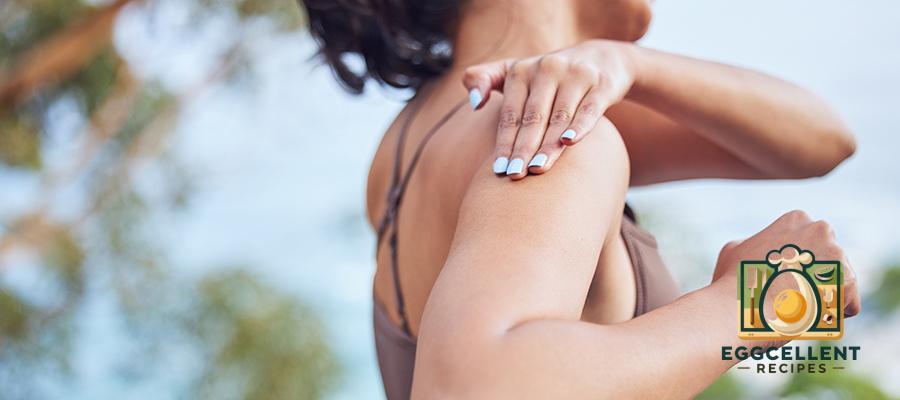

- Stiffness or swelling in joints
- Muscle cramps or aches
- Increased discomfort after consuming gluten-rich foods
Why it happens: Some people with gluten intolerance experience an inflammatory response that affects their joints and muscles, mimicking symptoms of arthritis.
5. Skin Issues
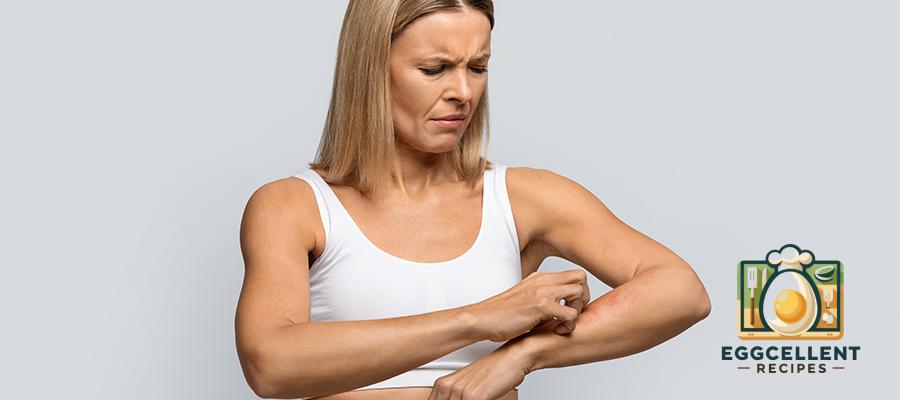

- Red, itchy rashes
- Dry or flaky skin
- Acne breakouts
- Eczema or psoriasis flare-ups
Why it happens: Gluten sensitivity may contribute to inflammatory skin conditions, as the body reacts negatively to the protein.
6. Mood Changes and Anxiety
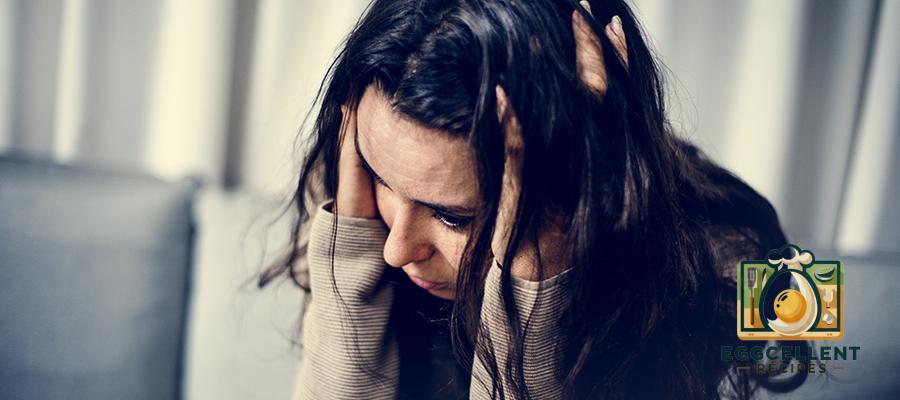

- Increased feelings of anxiety or panic
- Depression or mood swings
- Irritability or unexplained emotional distress
Why it happens: The gut and brain are closely connected, and inflammation from gluten sensitivity can impact neurotransmitter balance, leading to mood disturbances.
7. Unexplained Weight Changes
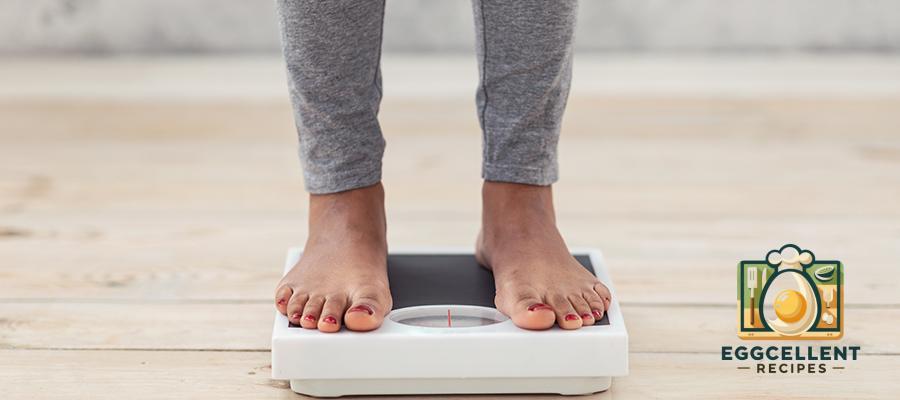

- Sudden weight gain or loss
- Difficulty maintaining a stable weight
- Loss of appetite or cravings for carbohydrate-rich foods
Why it happens: Gluten intolerance can interfere with nutrient absorption, digestion, and metabolism, leading to unexplained weight fluctuations.
8. Autoimmune Symptoms
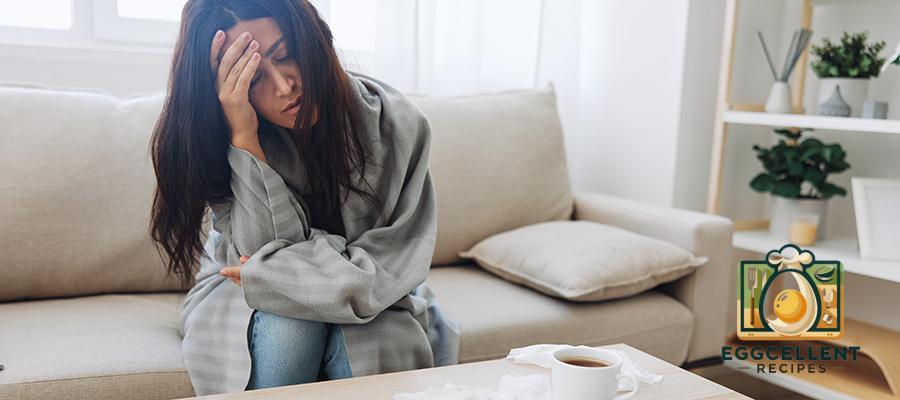

- Increased inflammation or flare-ups of autoimmune conditions
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (thyroid-related fatigue and weight gain)
- Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms worsening after gluten consumption
Why it happens: Gluten has been linked to increased immune system activity, which can exacerbate autoimmune conditions.
How to Determine if You Have Gluten Intolerance
1. Try an Elimination Diet
- Remove gluten from your diet for at least 2–4 weeks.
- Monitor symptoms to see if they improve.
- Slowly reintroduce gluten and observe any reactions.
2. Get Tested for Celiac Disease
- If you suspect gluten sensitivity, rule out celiac disease with a blood test.
- Celiac disease can cause long-term damage to the intestines, so proper diagnosis is essential.
3. Keep a Food and Symptom Journal
- Write down everything you eat and how you feel afterward.
- Look for patterns related to gluten consumption.
4. Consult a Healthcare Professional
- If you experience persistent symptoms, see a doctor or dietitian for further evaluation.
- A healthcare provider can help determine if your symptoms are due to gluten intolerance, another food sensitivity, or an underlying condition.
Final Thoughts
Gluten intolerance can manifest in various ways, from digestive distress to brain fog and skin issues. If you suspect gluten may be affecting your health, keeping track of symptoms and experimenting with a gluten-free diet can provide valuable insights. However, it’s important to seek professional guidance for an accurate diagnosis and long-term dietary planning.
By identifying and addressing gluten intolerance early, you can take proactive steps to improve your well-being, reduce inflammation, and enjoy a healthier, symptom-free life.
Would you like meal ideas or gluten-free alternatives? Let me know!