
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential fats that play a crucial role in maintaining overall health. They are important for brain function, heart health, reducing inflammation, and even supporting eye health. Since our bodies cannot produce omega-3s on their own, we must obtain them through our diet. Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your daily meals can help you meet your body’s needs and improve your well-being. In this article, we’ll explore some of the best food sources of omega-3s and their health benefits.
What Are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat, and there are three main types:
- ALA (Alpha-linolenic acid): Found mainly in plant-based foods like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts.
- EPA (Eicosapentaenoic acid): Found in fish and seafood, this type of omega-3 is beneficial for heart health and reducing inflammation.
- DHA (Docosahexaenoic acid): Also found in fish and seafood, DHA is crucial for brain development, cognitive function, and eye health.
To get the most benefits from omega-3s, it’s important to consume a variety of foods that provide these essential fatty acids.
Best Omega-3 Rich Foods
1. Salmon
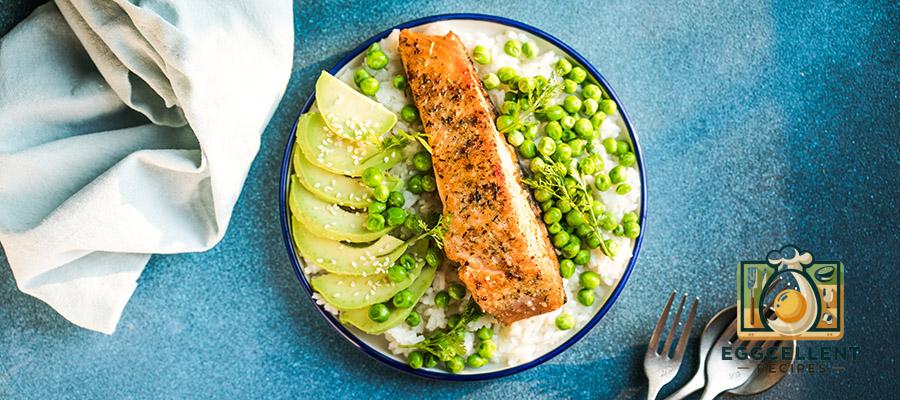

Benefits: Salmon is one of the richest sources of EPA and DHA omega-3s, making it a heart-healthy food choice. Regular consumption of salmon can help reduce inflammation, lower the risk of heart disease, and support brain health.
How to Eat: Grill, bake, or poach salmon for dinner, or add it to salads, grain bowls, or sandwiches.
2. Chia Seeds
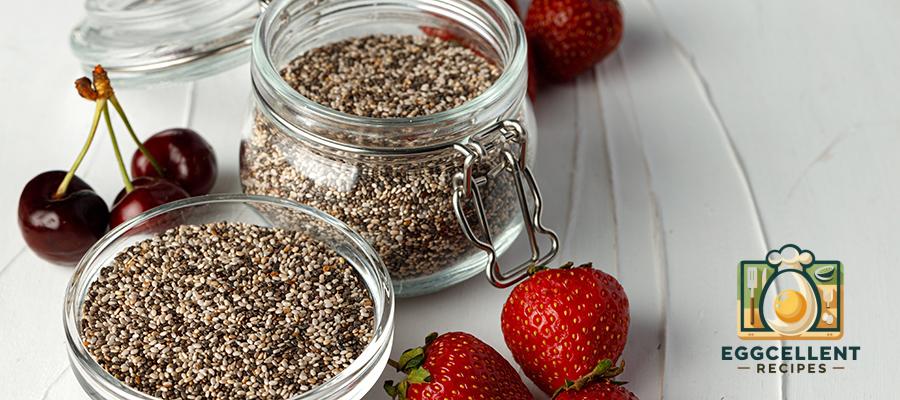

Benefits: Chia seeds are packed with ALA, the plant-based form of omega-3s, and are also high in fiber and protein. These tiny seeds can help reduce inflammation, support heart health, and improve digestion.
How to Eat: Add chia seeds to smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, or make chia pudding by soaking them in milk overnight.
3. Flaxseeds
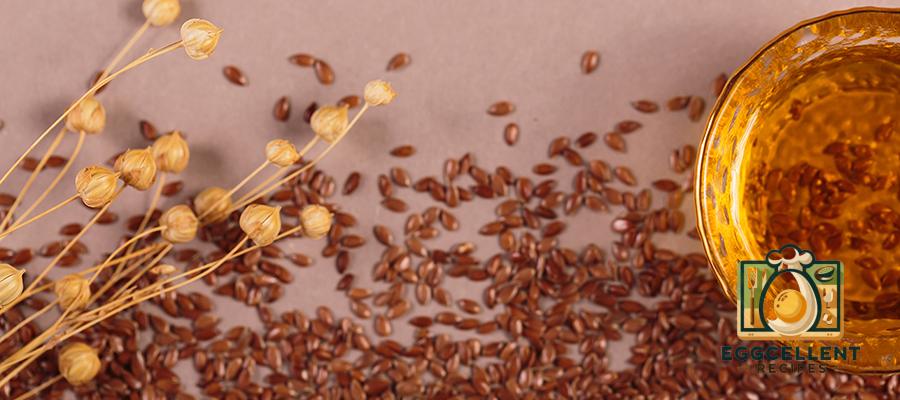

Benefits: Flaxseeds are another excellent plant-based source of ALA omega-3s. They also contain fiber and antioxidants that support digestive health and help lower cholesterol levels.
How to Eat: Add ground flaxseeds to smoothies, baked goods, or sprinkle them over cereal or salads.
4. Mackerel
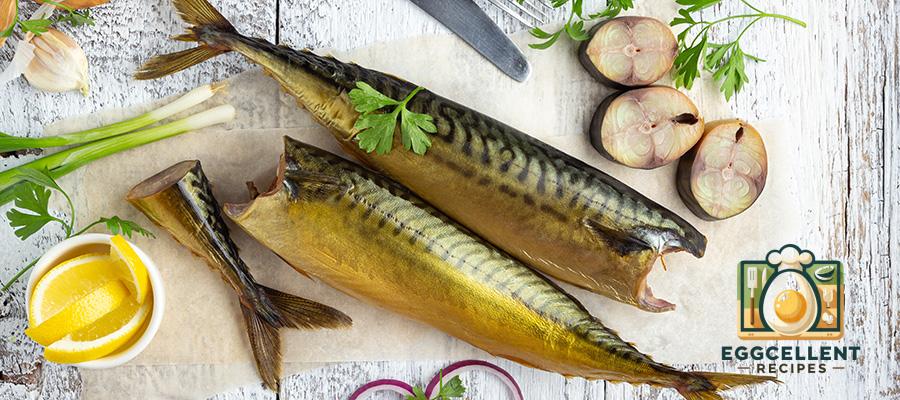

Benefits: Mackerel is a fatty fish rich in EPA and DHA omega-3s, known for its heart-healthy and anti-inflammatory properties. It’s also a good source of protein and vitamin D.
How to Eat: Grill or bake mackerel fillets, or enjoy canned mackerel in salads and sandwiches.
5. Walnuts
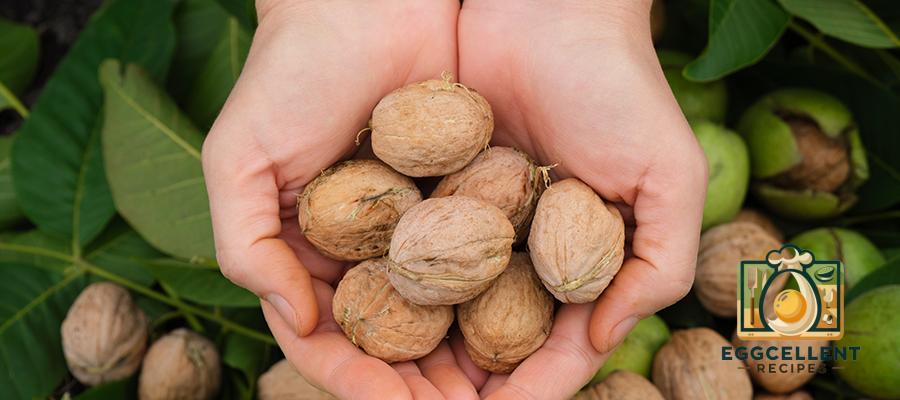

Benefits: Walnuts are an excellent source of ALA omega-3s and provide a healthy dose of antioxidants, fiber, and plant-based protein. They can help reduce inflammation and improve brain function.
How to Eat: Snack on walnuts, add them to salads, oatmeal, or incorporate them into baking.
6. Sardines
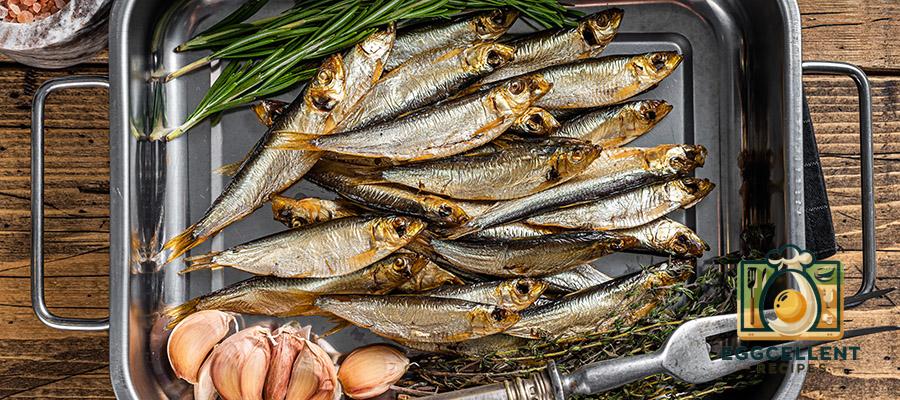

Benefits: Sardines are packed with EPA and DHA omega-3s, and they’re also a great source of calcium and vitamin D. These small fish are affordable, sustainable, and highly nutritious.
How to Eat: Enjoy sardines on toast, in salads, or mixed with pasta for a quick and nutritious meal.
7. Hemp Seeds
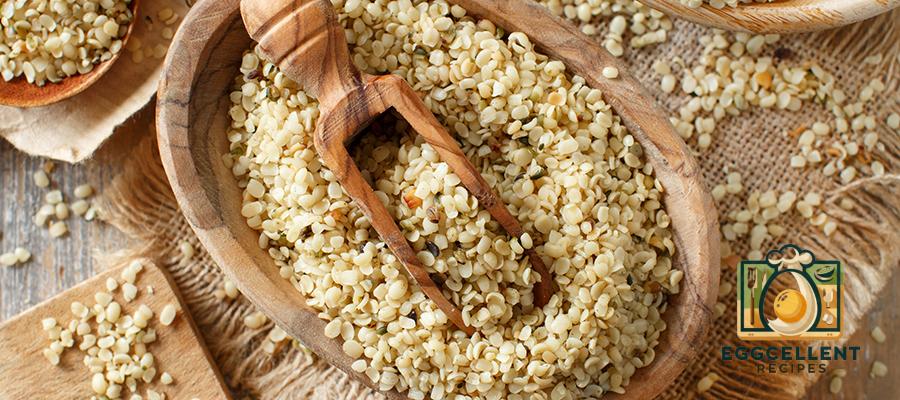

Benefits: Hemp seeds are rich in ALA omega-3s, and they also provide a balance of omega-6 fatty acids, which are important for heart health and inflammation reduction.
How to Eat: Sprinkle hemp seeds over yogurt, oatmeal, or salads, or add them to smoothies.
8. Algal Oil

Benefits: Algal oil is derived from algae and is one of the few plant-based sources of DHA and EPA omega-3s. It’s a great option for vegetarians and vegans who want to increase their omega-3 intake without eating fish.
How to Eat: Algal oil is available as a supplement and can be used as a substitute for fish oil. Add it to smoothies or take it in capsule form.
9. Cod Liver Oil
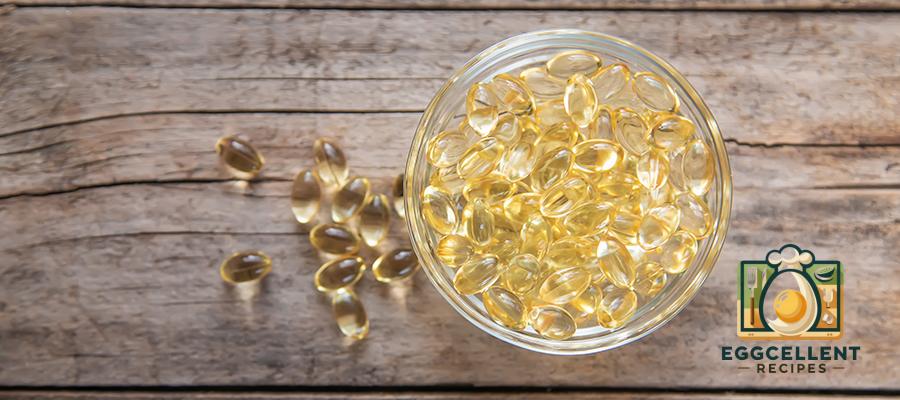

Benefits: Cod liver oil is not only rich in omega-3s (EPA and DHA) but also provides high levels of vitamins A and D, making it a powerful supplement for overall health. It’s particularly beneficial for heart and joint health.
How to Eat: Cod liver oil is typically consumed as a supplement. You can take it in liquid form or as capsules, as directed on the packaging.
10. Anchovies
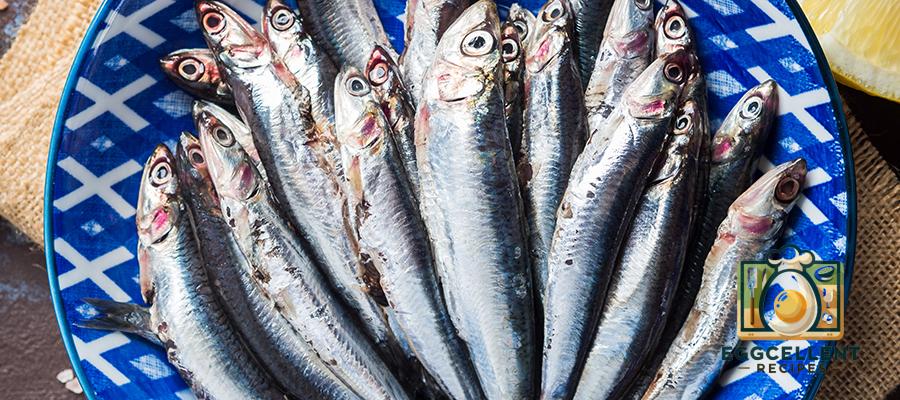

Benefits: Anchovies are small, oily fish that are packed with omega-3s, as well as protein, calcium, and iron. They are a great addition to a Mediterranean-style diet and can help reduce inflammation.
How to Eat: Add anchovies to salads, pizza, pasta sauces, or use them in dressings for a rich, savory flavor.
11. Brussels Sprouts
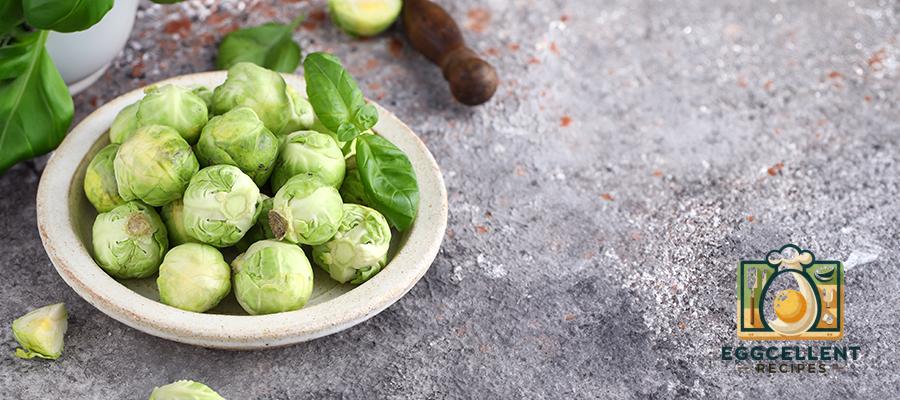

Benefits: Brussels sprouts are a surprising source of ALA omega-3s, especially for a vegetable. They also provide fiber, vitamins C and K, and antioxidants that support overall health.
How to Eat: Roast or sauté Brussels sprouts as a side dish, or add them to grain bowls and salads.
12. Eggs (Omega-3 Enriched)
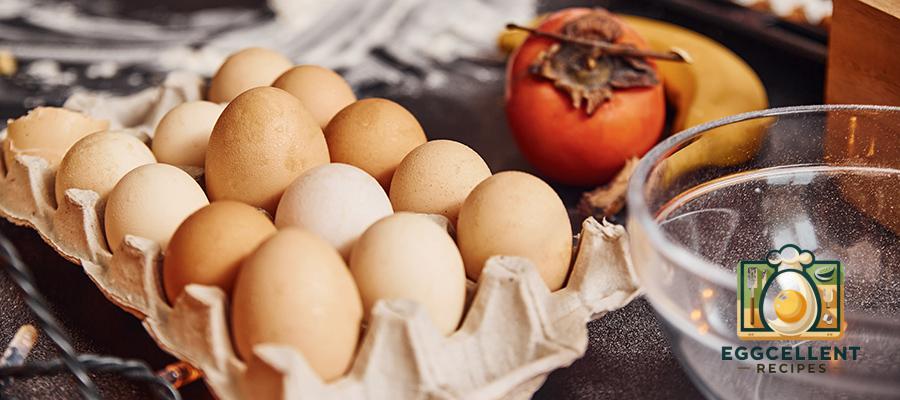

Benefits: Omega-3-enriched eggs come from hens that are fed a diet rich in flaxseeds or fish oil, which increases the omega-3 content of the eggs. These eggs are a convenient way to boost your omega-3 intake.
How to Eat: Use omega-3 eggs in any recipe that calls for eggs, such as omelets, scrambled eggs, or baked goods.
13. Seaweed and Algae
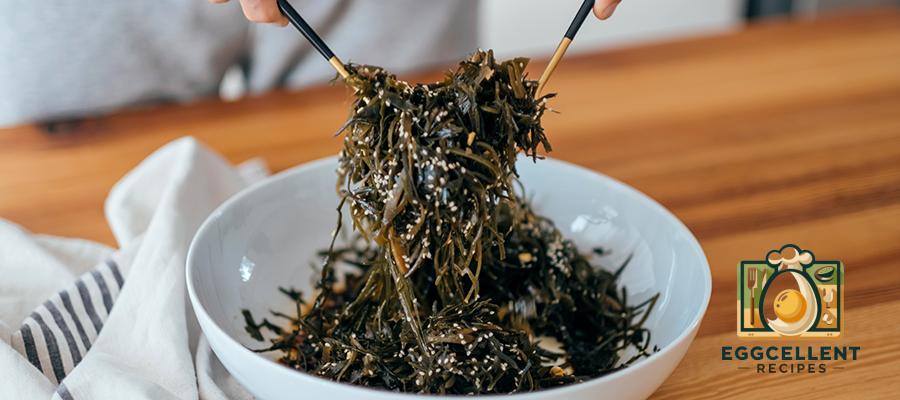

Benefits: Seaweed and algae, like spirulina and chlorella, are rich in omega-3s, particularly DHA. They are also nutrient-dense, providing vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support brain and heart health.
How to Eat: Add seaweed to salads, sushi, or miso soup, or take spirulina or chlorella supplements in powder or capsule form.
14. Edamame (Young Soybeans)
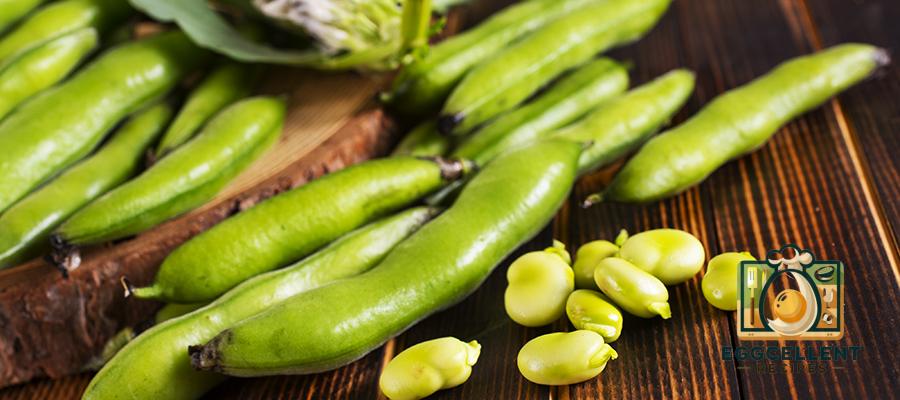

Benefits: Edamame is a plant-based source of ALA omega-3s and is also rich in protein, fiber, and vitamins. It makes a healthy and convenient snack or side dish.
How to Eat: Enjoy steamed edamame as a snack or add it to stir-fries, grain bowls, or salads.
15. Grass-Fed Beef
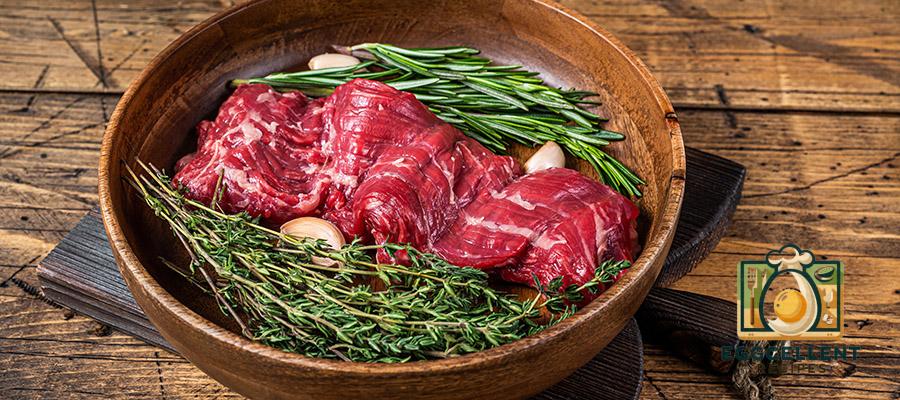

Benefits: Grass-fed beef contains more omega-3 fatty acids compared to conventionally raised beef. It also provides high-quality protein, iron, and other essential nutrients.
How to Eat: Grill or roast grass-fed beef as part of a balanced meal with plenty of vegetables and whole grains.
Health Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Incorporating omega-3-rich foods into your diet can provide numerous health benefits, including:
- Heart Health: Omega-3s are known to lower triglycerides, reduce blood pressure, and decrease the risk of heart disease.
- Brain Function: DHA is critical for brain development and function, and it may help prevent cognitive decline as you age.
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: Omega-3s help reduce inflammation, which can lower the risk of chronic diseases like arthritis, diabetes, and cancer.
- Eye Health: DHA supports the development and maintenance of healthy vision, and omega-3s may reduce the risk of age-related macular degeneration.
- Mental Health: Omega-3s, particularly EPA, have been shown to reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Final Thoughts
Omega-3 fatty acids are essential for maintaining good health, and incorporating a variety of omega-3-rich foods into your diet is one of the best ways to ensure you’re meeting your body’s needs. Whether you enjoy fatty fish like salmon, plant-based sources like flaxseeds and walnuts, or supplements like cod liver oil and algal oil, adding omega-3s to your meals can boost your heart, brain, and overall health.
By making small changes to your diet and incorporating these omega-3-rich foods, you can enjoy the benefits of better health and well-being. Remember, a balanced diet with a variety of nutrient-dense foods is key to achieving long-term wellness.






One Response